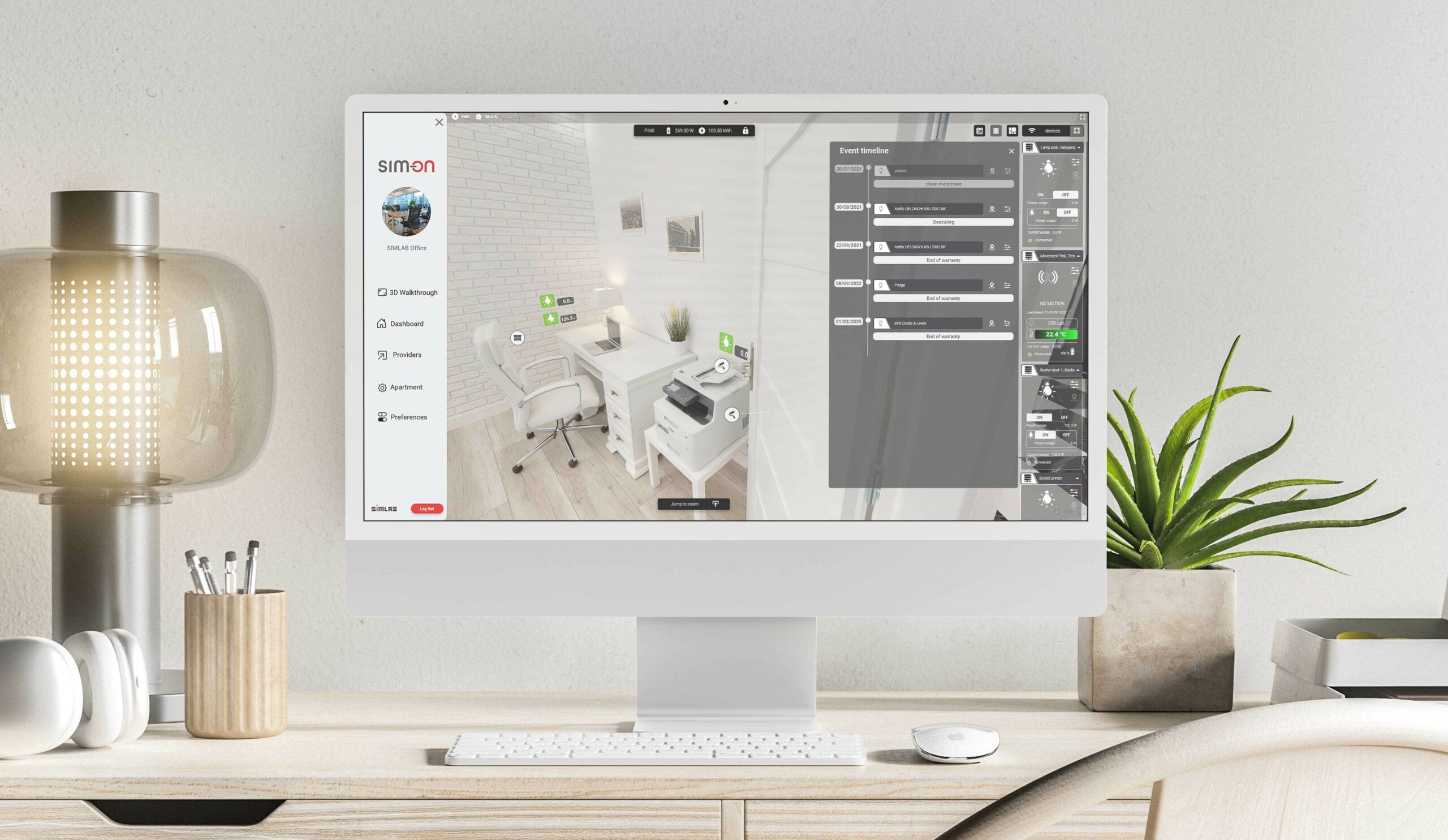
27 Jul A digital twin of a KNX-based property with KNX IoT
Data analytics, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things are three developing industries that have embraced the usage of digital twin technology beyond manufacturing. As increasingly complex “things” become connected and have the capacity to provide data, having a digital twin enables data scientists and other IT specialists to optimize deployments for optimal efficiency and create multiple what-if scenarios.
To know more about digital twin, examples of digital twin, and their application, continue reading through this article
What is a digital twin
A digital twin is a representation of an actual object, service, or process in the digital world. A digital twin can be a representation of a real-world object, such as a wind farm, jet engine, or even larger objects like a building or the whole city.
In general, a digital twin is a computer software that simulates how a process or product would work using data from the real world. These applications can use artificial intelligence, software analytics, and the internet of things to enhance productivity.
Applications of the digital twin
Digital twin technology has been adopted in various fields or industries to solve different problems. Examples of industries that have adopted the use of digital twin are:
Manufacturing Industries
The manufacturing sector uses digital twins the most extensively. The production of digital twins is facilitated by the use of expensive equipment that produces a large amount of data. Manufacturing industries use digital twin in developing their products, customizing the product design, market prediction and analysis, and all the processes in between.
Healthcare
Just like with products, digital twins can be used to profile patients seeking medical treatment. The same sensor-generated data system may monitor many health parameters and generate critical insights.
Automotive Industries
The majority of new automotive development occurs in a virtual environment. In the automotive industry, digital twins are utilized to build a virtual representation of a related vehicle. Even before production begins, automobile companies use technology to build the ultimate car product. They model and examine the manufacturing process and potential issues when the vehicle is serviced.
Urban planning
Civil engineers and other people involved in urban planning can benefit greatly from using digital twins, which can show 3D and 4D spatial data in real time and incorporate augmented reality systems in constructed environments.
Types of digital twins
Primarily there are four types of digital twins
Component twin
Digital representations of a specific component of a system or product, like a gear or screw. Component twins are often used to represent integral parts, such as those under specific stress or heat, instead of merely modelling all the various parts of a product. Designers and engineers can understand how the parts can be modified to maintain their integrity in likely circumstances by digitally modelling them and exposing them to dynamic simulations.
Asset twin
Asset twins, also known as product twins, are digital replicas of a whole product rather than just its parts. Asset twins are technically made up of many component twins, but their main goal is to show how the many pieces of a real-world product work together. For instance, a wind turbine might have a corresponding asset twin to track its performance and spot potential component breakdown due to normal wear and tear.
System twin
System twins, also known as unit twins, are digital representations of product systems in action. System twins simulate these separate products as pieces of a larger system, whereas asset twins simulate real-world products made up of numerous parts. It is possible to enhance the relationships between assets by having a better understanding of how they interact, which will boost productivity and efficiency.
Process twin
Digital representations of interconnected systems are called process twins. For instance, a process twin could model the complete factory down to the employees working the machinery on the factory floor, whereas a system twin might simulate a production line.
About digital twin markets
The global digital twin market study share is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 60.6% from 2017 to 2027, reaching USD 73.5 billion. The market has a high growth potential since manufacturing businesses focus more on the digital twin to cut costs and enhance supply chain operations. The demand for digital twins is rising in the healthcare sector, and the market is expanding as predictive maintenance is given more attention.
Advantages of the digital twins
For the past 8-year digital twin has been very beneficial to all industries that utilize the technology, the advantage of digital twin include;
Improves financial decision-making process
Financial information, such as the price of materials and labour, can be incorporated into a virtual representation of a physical object. Due to the availability of a sizable amount of real-time data and powerful analytics, businesses may be able to make decisions regarding whether changes to a manufacturing value chain are financially viable more rapidly and effectively..
Increased client satisfaction
Digital twins can facilitate more efficient customer service and repair processes while guiding future product improvements because they collect real-time data about the product. Predictive maintenance is one application where digital twins can improve customer satisfaction.
Improves the quality of the product
This advantage develops over time as data is gathered via a digital twin. After early investments have been made, engineers and designers can use generational enhancements of a product based on real-world operational data from numerous digital twins to guide the creation of a new product or version.
Examples and use cases of digital twins
Aviation
A use case is the Rolls-Royce
Rolls-Royce, a significant player in the aerospace industry, uses digital twin technology to experiment with different engine designs and inspection procedures. Before moving on with the development of the physical model, aviation engineers can test the limits and maintenance needs of an engine prototype using digital twin models.
Oil
A use case is the infrotrax Engineering.
VAM2, a digital twin solution created by SaaS company Infotrax Engineering, is excellent for managing offshore oil and gas operations. Remote access to the most recent information on the state of the plant has never been more straightforward, thanks to the digital twin tool. Managers can conduct safety inspections and other maintenance procedures at scale because physical assets are evaluated and documented in real time.
Healthcare
A use case is the circuit stream.
Circuit Stream’s immersive AR/VR Unity course is an intelligent method to educate future medical professionals. Students are introduced to a virtual chemistry lab in this brief 1.5-hour online class, where they can conduct experiments securely without running the risk of being exposed to dangerous chemicals or open flames.
Collaborate with KNX IoT
Collaboration and innovative thinking were essential in this case study of the development of a digital twin solution based on KNX IoT. Since we at KNX think that shared goals and growth will lead to the development of more sustainable, inclusive, and effective solutions, we actively promote these principles. We cordially invite both KNX members and non-members to use KNX IoT to enter the IoT ecosystem.

